*This post may contain affiliate links for which I earn commissions.*
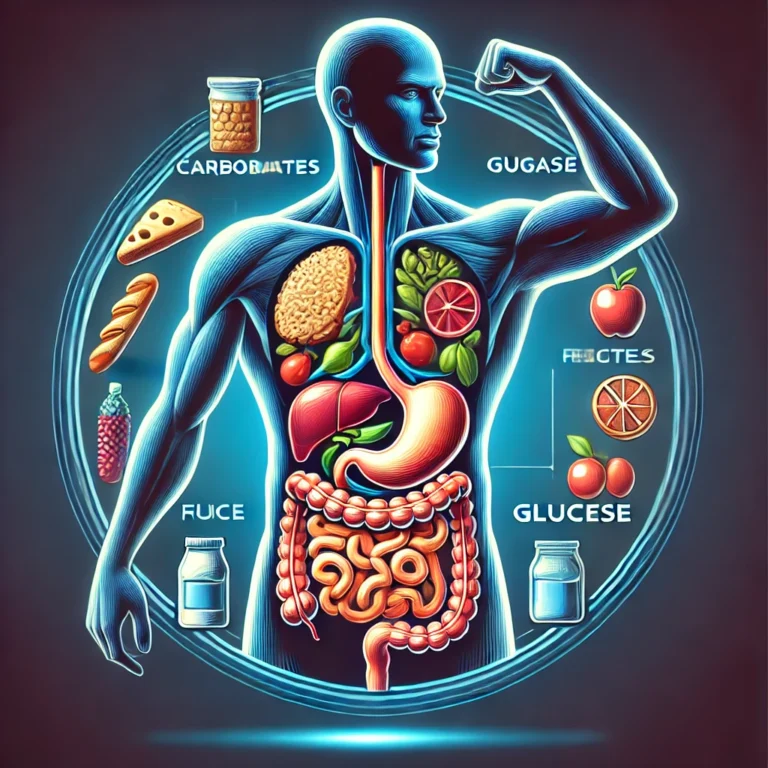
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It’s a disease where the body either doesn’t produce enough insulin or can’t effectively use the insulin it does produce. Insulin is crucial because it helps convert sugar, or glucose, from food into energy. Without proper insulin function, glucose builds up in the blood, leading to serious health problems.
There are three main types of diabetes: Type 1, Type 2, and gestational diabetes. Type 1 diabetes is often diagnosed in children and young adults and is characterized by the body’s inability to produce insulin. Individuals with Type 2 diabetes, the most common form, either don’t produce enough insulin or their bodies resist the insulin they do make. Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy and usually goes away after giving birth but increases the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes later on.
The prevalence of diabetes is alarming. It’s estimated that over 400 million people live with diabetes globally, and this number is rising. Poor diet, lack of exercise, and obesity are significant contributors to this epidemic. But it’s not just a modern problem; genetics also play a role, making some people more predisposed to developing the condition than others.
Early diagnosis and management of diabetes are essential. Many people live with diabetes for years without realizing it. Routine check-ups can catch high blood sugar levels before they lead to more severe complications such as heart disease, kidney failure, and vision problems. Recognizing symptoms like excessive thirst, frequent urination, unexplained weight loss, and fatigue can prompt seeking medical advice sooner.
Living with diabetes requires a holistic approach to health. Managing the condition is about regular monitoring, making informed food choices, staying active, and taking prescribed medications. It’s also about staying educated and supported, whether through healthcare professionals, family, or diabetes support groups.
Understanding the Causes of Diabetes
Diabetes emerges from a complex interplay of factors. While genetics can lay the groundwork, lifestyle and environmental influences often act as the final push toward developing the condition.
Genetic factors play a significant role. If you have a family history of diabetes, the likelihood of developing it increases. Researchers have identified multiple genes tied to Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes, which can either directly cause the disease or increase susceptibility.
Lifestyle choices are another major contributor. Diets high in processed foods, sugars, and unhealthy fats can lead to obesity, a key risk factor for Type 2 diabetes. Physical inactivity compounds this risk, as regular exercise helps regulate blood sugar levels and maintain a healthy weight.
Environmental triggers also have a part to play. Exposure to certain viruses might trigger the immune response that leads to Type 1 diabetes. Additionally, factors such as stress and poor sleep can negatively impact blood sugar control, adding another layer of complexity to managing the disease.
Understanding these causes is crucial for prevention and management. For those with a genetic predisposition, early lifestyle interventions can make a significant difference. Adopting a diet rich in whole foods, staying active, and maintaining a balanced life can help mitigate the risk.
Education and awareness are your best defense against diabetes. By recognizing the various factors that contribute to the disease, you can take proactive steps to protect your health. Regular medical check-ups, being mindful of your diet, and integrating physical activity into your routine are practical ways to stay ahead.
Current Treatment Options
Managing diabetes involves a multi-faceted approach tailored to individual needs. Medications, dietary changes, exercise, and regular monitoring form the cornerstone of effective management.
Medication is often necessary for diabetes control. People with Type 1 diabetes require insulin therapy since their bodies can’t produce insulin. There are various forms of insulin available, including rapid-acting, long-acting, and intermediate-acting, administered through injections or insulin pumps. For those with Type 2 diabetes, oral medications like metformin can help control blood sugar levels by improving the body’s insulin sensitivity or reducing glucose production in the liver.
Diet is another crucial element. Eating balanced meals with a focus on whole grains, lean proteins, vegetables, and healthy fats can help manage blood sugar levels. Monitoring carbohydrate intake is especially important since carbs have a direct impact on glucose levels. Working with a dietitian can provide personalized guidelines to optimize blood sugar control.
Physical activity plays a vital role in managing diabetes. Regular exercise helps lower blood sugar, improves insulin sensitivity, and supports overall well-being. Activities such as walking, swimming, and strength training can be beneficial. Finding an exercise routine that you enjoy and can stick with is key to making it a permanent part of your lifestyle.
Regular monitoring is essential in diabetes management. Keeping track of blood sugar levels helps you understand how your body responds to different foods, activities, and medications. Many people use glucose meters or continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) to keep a close watch on their levels. Frequent monitoring provides the data needed to make informed decisions about diet, activity, and medication adjustments.
Support from healthcare professionals is invaluable. Endocrinologists, diabetes educators, dietitians, and primary care physicians work together to provide comprehensive care. They help tailor treatments and offer guidance on managing daily challenges. Don’t hesitate to reach out to them with questions or for adjustments in your management plan.
The Concept of ‘Cure’ vs. Management
When discussing diabetes, the terms ‘cure’ and ‘management’ often get entangled, but they hold different meanings. Understanding this distinction is vital for setting realistic expectations and goals.

In medical terms, a ‘cure’ implies completely eradicating the disease from the body, leading to a state where no further treatment is necessary. For diabetes, this would mean the continuous and effortless maintenance of normal blood sugar levels without medication or lifestyle interventions.
However, current medical consensus indicates that a definitive cure for diabetes remains elusive. This is partly because diabetes involves complex disruptions in how the body regulates blood sugar.
Effective management, on the other hand, focuses on maintaining blood sugar levels within a target range and preventing complications. This generally involves a combination of medication, diet, exercise, and regular monitoring. While it may not eliminate the disease, effective management can lead to a healthy, balanced life.
There’s also the concept of remission, which means that blood sugar levels have returned to normal ranges without the need for medication. In cases of Type 2 diabetes, significant lifestyle changes can sometimes achieve remission, leading to periods where the condition seems ‘cured’. However, this state requires ongoing vigilance, as blood sugar levels can rise again.
Various research studies have explored potential cures. For instance, some people with Type 1 diabetes have maintained normal blood sugar levels for years following a pancreas transplant. Similarly, weight-loss surgery has led to remission in some cases of Type 2 diabetes. However, these approaches are not universally applicable and come with their own risks and costs.
Recognizing the difference between a cure and effective management empowers individuals with realistic goals and actionable plans. Achieving optimal blood sugar control and reducing the risk of complications should be the primary focus. This involves a holistic approach, combining medical treatment, lifestyle changes, and education to navigate the complexities of diabetes.
Scientific Advances in Diabetes Research
The search for a diabetes cure has sparked numerous scientific advances, making treatment more effective and manageable. Breakthroughs in genetic research have uncovered specific genes linked to diabetes, opening doors for gene therapy. Researchers are exploring ways to edit these genes to either prevent or reverse the condition.
Stem cell therapy is another promising area of research. Scientists are investigating how stem cells can be programmed to develop into insulin-producing cells. This has the potential to restore the pancreatic function in people with Type 1 diabetes. While still in experimental stages, stem cell therapy could revolutionize treatment in the future.
Regenerative medicine is pushing boundaries too. Techniques like islet cell transplantation, where clusters of cells are transplanted into the liver, aim to replace the faulty insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. Early results show promise, but challenges like ensuring long-term survival and function of these cells remain.
Innovations in technology have also significantly impacted diabetes management. Artificial pancreas systems, which combine continuous glucose monitors (CGM) and insulin pumps, are advancing. These systems can automatically check blood glucose levels and deliver the right amount of insulin, closely mimicking the body’s natural processes.
Wearable devices like smartwatches are being integrated with diabetes management apps. These offer real-time data tracking and support, providing users with instant feedback and guidance. Enhanced data analytics can predict blood sugar trends and offer personalized insights, making diabetes management more intuitive.
The exploration of gut microbiota holds promise as well. Researchers are studying how the bacteria in our intestines impact insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism. This could lead to new treatments targeting gut health to improve diabetes outcomes.
Staying informed about these scientific advancements can help you make better decisions about your healthcare plan. Emerging therapies and technologies bring hope, but it’s crucial to consult healthcare professionals to understand how these innovations fit into your personal treatment.
Alternative and Complementary Approaches
People often seek out alternative and complementary approaches to supplement traditional diabetes treatments. These methods can offer additional support but should be used responsibly and in consultation with healthcare providers.
Herbal remedies have gained popularity for their potential to stabilize blood sugar levels. For example, fenugreek seeds, bitter melon, and berberine have shown promise in small studies. However, the efficacy and safety of these herbs can vary, and they should not replace prescribed medications.
Acupuncture is another alternative therapy that some find beneficial. It’s believed to improve insulin sensitivity and promote relaxation, helping manage stress levels. While not a cure, acupuncture can be a valuable component of a holistic diabetes care plan.
Traditional medicine, such as Ayurveda and Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), offers various treatment options based on ancient practices. These approaches often emphasize lifestyle, dietary changes, and herbal treatments. While they can provide some benefits, it’s essential to evaluate their scientific backing and integrate them cautiously with modern treatments.
Mind-body practices like yoga and meditation are highly recommended for diabetes management. These practices reduce stress, improve mental well-being, and may enhance insulin sensitivity. Yoga, in particular, involves physical activity that can help maintain a healthy weight and promote overall health.
Supplements, including magnesium and chromium, are sometimes used to support diabetes management. Some studies suggest they may help improve blood sugar control, but it’s essential to discuss their use with a healthcare provider to avoid potential interactions or side effects.
Combining alternative approaches with conventional treatments can be beneficial. However, it’s crucial to remain informed and skeptical of any ‘miracle cures,’ often lacking scientific validation. A balanced, well-researched approach will offer the best chance for effective diabetes management. Consulting with healthcare professionals ensures these complementary methods are safely and effectively integrated into your treatment plan.
Lifestyle Changes and Prevention
Preventing diabetes or managing it effectively often boils down to making sustainable lifestyle changes. A balanced diet, regular physical activity, and managing stress are key components.
Incorporating a balanced diet is one of the most impactful steps you can take. Focus on whole foods, including plenty of vegetables, fruits, lean proteins, and whole grains. Reducing intake of processed foods and sugary drinks can help keep blood sugar levels steady. Keeping portion sizes in check and eating at regular intervals also supports a balanced blood sugar level.
Physical activity is equally important. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week. Activities like brisk walking, cycling, swimming, or even dancing can help manage blood sugar and maintain a healthy weight. Strength training exercises are also beneficial as they build muscle mass, which improves insulin sensitivity.
Stress has a direct impact on blood sugar levels, making stress management crucial. Techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and mindfulness can help keep stress levels in check. Even simple activities like spending time in nature or engaging in hobbies can make a difference.
Ensuring adequate sleep is another vital aspect of diabetes prevention and management. Poor sleep can adversely affect blood sugar levels and overall health. Aim for 7 to 9 hours of quality sleep per night. Creating a sleep-friendly environment and maintaining a consistent sleep schedule can enhance sleep quality.
Regular health check-ups are essential for early detection and management of diabetes. Routine screenings like fasting blood sugar tests or HbA1c tests can catch issues early, allowing timely intervention. If you have risk factors, such as a family history of diabetes, discussing preventive measures with your healthcare provider is wise.
Education is a powerful tool in diabetes prevention. Staying informed about the disease, its risk factors, and management strategies enables you to take proactive steps. Consider joining diabetes education programs or support groups to stay motivated and knowledgeable.
By making these lifestyle changes, you can significantly reduce your risk of developing diabetes or better manage the condition if you already have it. The effort invested in adopting a healthier lifestyle pays off in long-term health benefits.
Living with Diabetes: Patient Stories
Hearing from others who have faced similar challenges can be incredibly motivating and insightful. Patient stories offer real-life perspectives on managing diabetes, overcoming obstacles, and achieving personal goals.
One inspiring example is Jane, a Type 1 diabetic who has run multiple marathons. Despite her diagnosis at a young age, Jane embraced exercise as a way to manage her condition. She diligently monitors her blood sugar levels and adjusts her insulin dosages to match her activity. Her story demonstrates that with careful planning and determination, it’s possible to pursue athletic ambitions while managing diabetes.
Another story comes from Tom, diagnosed with Type 2 diabetes in his forties. Initially overwhelmed, Tom attended a diabetes education program where he learned about diet, exercise, and medication management. By making incremental changes like substituting sugary drinks with water and incorporating daily walks, he saw significant improvements in his health. Tom’s journey emphasizes the power of education and small, consistent changes.
Emma’s experience with gestational diabetes during her pregnancy highlighted the importance of a supportive healthcare team. Working closely with her doctors and a dietitian, she followed a meal plan and monitored her blood sugar levels to ensure a healthy pregnancy. Post-pregnancy, she maintained these healthy habits, reducing her risk of developing Type 2 diabetes. Emma’s story underscores the value of professional guidance and long-term lifestyle adjustments.
These stories illustrate that while diabetes presents challenges, it doesn’t have to limit one’s life. The common thread in each journey is the proactive approach to managing the condition—staying informed, making healthy choices, and seeking support.
Living with diabetes requires resilience and adaptability. The experiences of others can provide valuable lessons and encouragement. Whether it’s learning new recipes, finding exercise routines that fit into a busy schedule, or navigating social situations with dietary restrictions, there’s a wealth of wisdom to draw from.
Support networks, be they in-person or online, play a crucial role in living well with diabetes. Joining local diabetes groups, participating in forums, or following inspiring diabetes bloggers can help you stay motivated and connected.
Ultimately, each person’s diabetes journey is unique, but the shared experiences and solutions provide a roadmap to living a full and active life. By seeking out and sharing these stories, you can find the inspiration and strategies needed to manage your own diabetes effectively.
Future Outlook: Can Diabetes Be Cured?
The quest to cure diabetes remains a dynamic area of medical research, with ongoing advancements offering hope for the future. Researchers are exploring various avenues, from cutting-edge technologies to novel treatments, aiming to get closer to a cure.
Current consensus within the medical community is that while a definitive cure for diabetes doesn’t exist yet, significant progress has been made in improving management and quality of life for those living with the condition. This progress fosters optimism that future breakthroughs might turn the dream of a cure into reality.
Gene therapy is one promising field. By targeting the genetic underpinnings of diabetes, scientists hope to develop treatments that can correct the root cause of the condition. Early-stage research shows potential, but it will likely be some time before these therapies are widely available.
Regenerative medicine, including stem cell research, also holds considerable promise. Efforts to regenerate insulin-producing cells in the pancreas could pave the way for treatments that restore normal insulin function. Trials and experiments continue to refine these approaches and address the challenges involved.
Technology, particularly artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning, is enhancing our understanding of diabetes. AI can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and predictors of blood sugar fluctuations, leading to more personalized and effective management strategies. Future applications may go beyond management, inching closer to preventive and curative solutions.
Lifestyle and preventive measures remain crucial. Advancements in understanding the interplay between diet, exercise, and diabetes risk can help shape guidelines that reduce the incidence of diabetes. Ongoing education and public health initiatives play a vital role in this endeavor.
The path to a cure involves not just scientific advancements but also public support and funding. Continued investment in diabetes research is essential for maintaining momentum and achieving breakthroughs. Public awareness campaigns and fundraising efforts significantly contribute to these goals.
While it’s important to remain cautiously optimistic, it’s equally vital for those living with diabetes to focus on current best practices for management. Adhering to medical advice, staying informed about new developments, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle create a strong foundation for future advancements.
In sum, while a cure for diabetes isn’t here yet, the scientific community is making meaningful strides. The future holds promise, and with continued research and support, the goal of curing diabetes moves closer. In the meantime, practical and proactive diabetes management strategies provide the best pathway to health and well-being.